5.1 KiB
title, description, published, date, tags, editor, dateCreated
| title | description | published | date | tags | editor | dateCreated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preparation | true | 2021-11-17T22:13:28.351Z | markdown | 2021-11-15T15:39:49.074Z |
Section under construction {.is-warning}
Prepare the host computer
Requirements
These instructions are valid for x86-64 computers that do ship with Linux or Windows.
Phyllome OS targets x86 systems with hardware-assisted virtualization, with a strong preference for those providing IOMMU as well.
It is expected that Phyllome OS will consume approximately 1 CPU core and 1 GB of RAM, which should be enough to accommodate a few virtual machines. For instance, on a system with a CPU with 4 cores and 8 GB of RAM, a guest virtual machine will be able to be assigned up to 3 cores and 7 GB of RAM.
Minimum requirements for Phyllome OS Desktop
- x86 computer that supports the first generation of hardware-assisted virtualization extensions
- For AMD-based configurations, it means that AMD V is available and enabled
- For Intel-based configurations, it means that Intel VT-x is available and enabled
- 2-core processor
- 8 GB of RAM
- SSD-based storage device to store disk images and Phyllome OS
- Any graphics card (Linux or macOS guests only)
Recommended requirements for Phyllome OS Desktop
- x86 computer that supports the second generation of hardware-assisted virtualization extensions
- For AMD-based configurations, it means that AMD Vi is available and enabled
- For Intel-based configurations, it means that Intel VT-d is available and enabled
- 8-core processor
- 16 GB of RAM
- NVME-based storage device to store disk images and Phyllome OS
- Two graphics cards or a graphics card that supports vfio-mdev or SR-IOV
Enable hardware-assisted virtualization
Access the firmware
The Open Virtual Machine Firmware (OVMF), which is based on the TianoCore firmware, is the default firmware for EFI-based virtual machines. It can be accessed using the Esc key.
- Since Windows 8: command-line instructions
Press the Win and X keys simultaneously to make a context menu appears. Then press Shift and a to politely ask Windows to open Powershell using elevated privileges, and click on the Yes button to bypass the User Account Control pop-up. Finally, input the following command inside the command prompt and press enter.
shutdown /fw /r
-
Since Windows 8: a visual walk-through
-
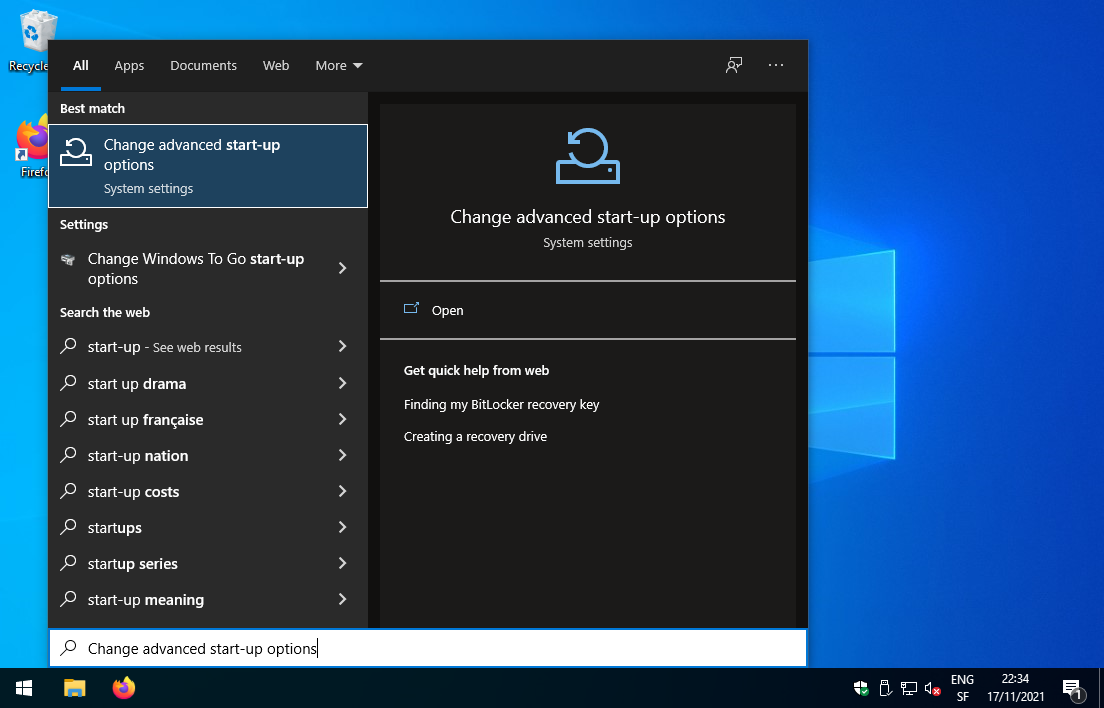
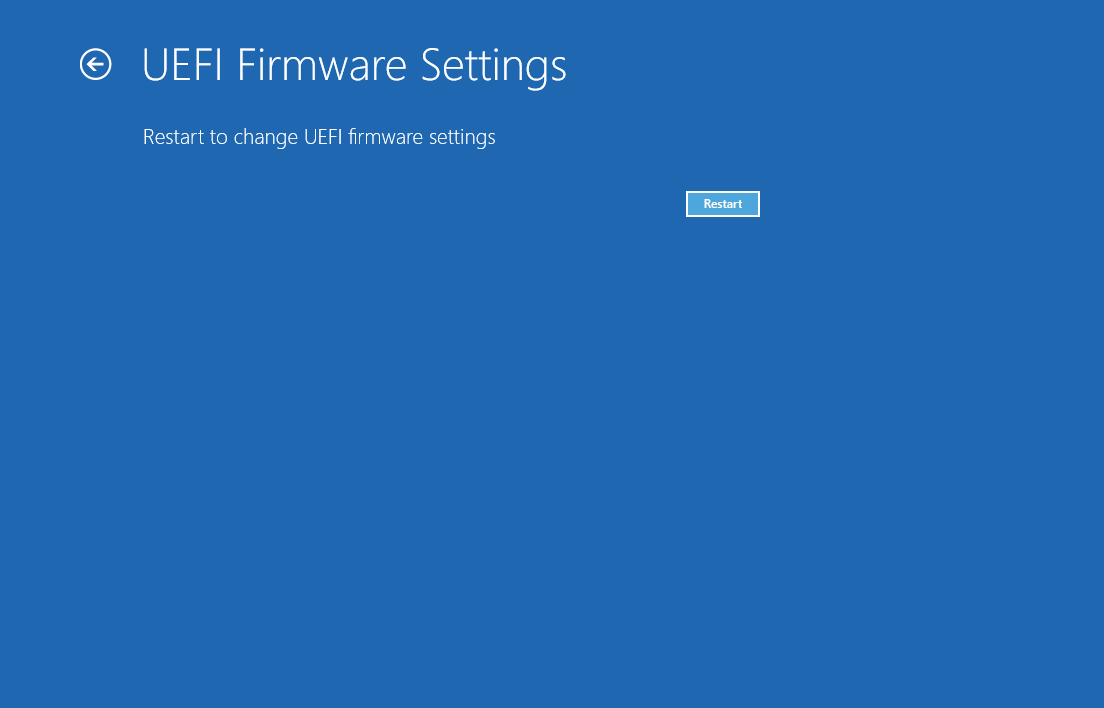
Open the start-up menu and write
start-up, then select Change advanced start-up options
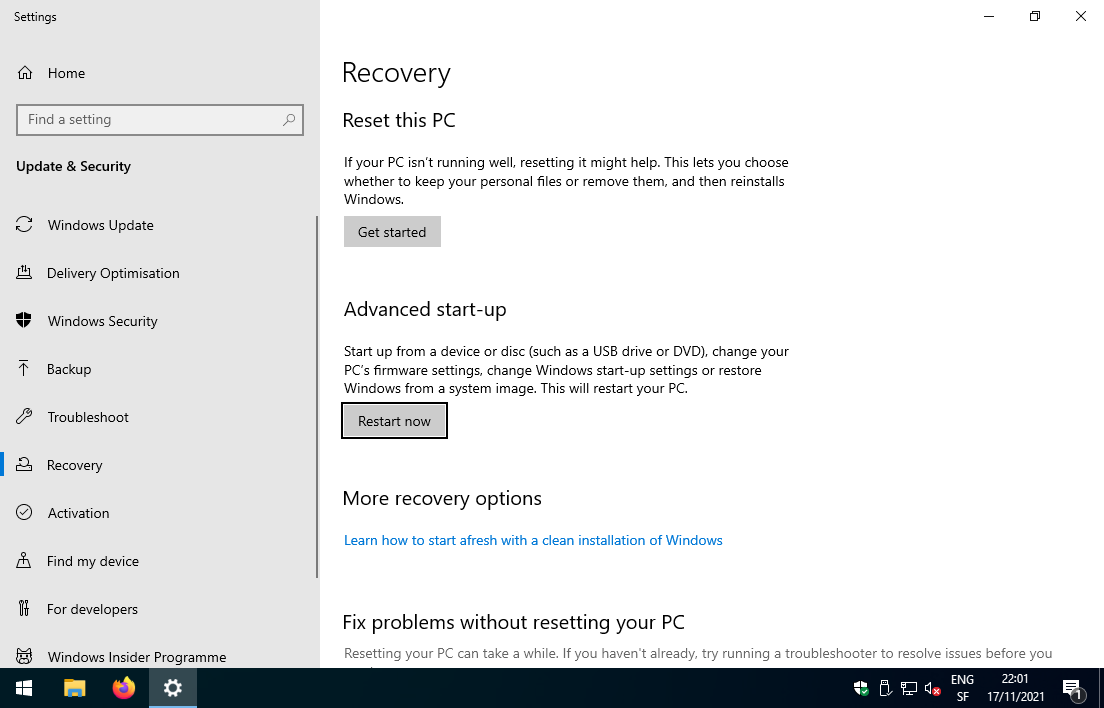
- Under the Advanced start-up section, click on
Restart now
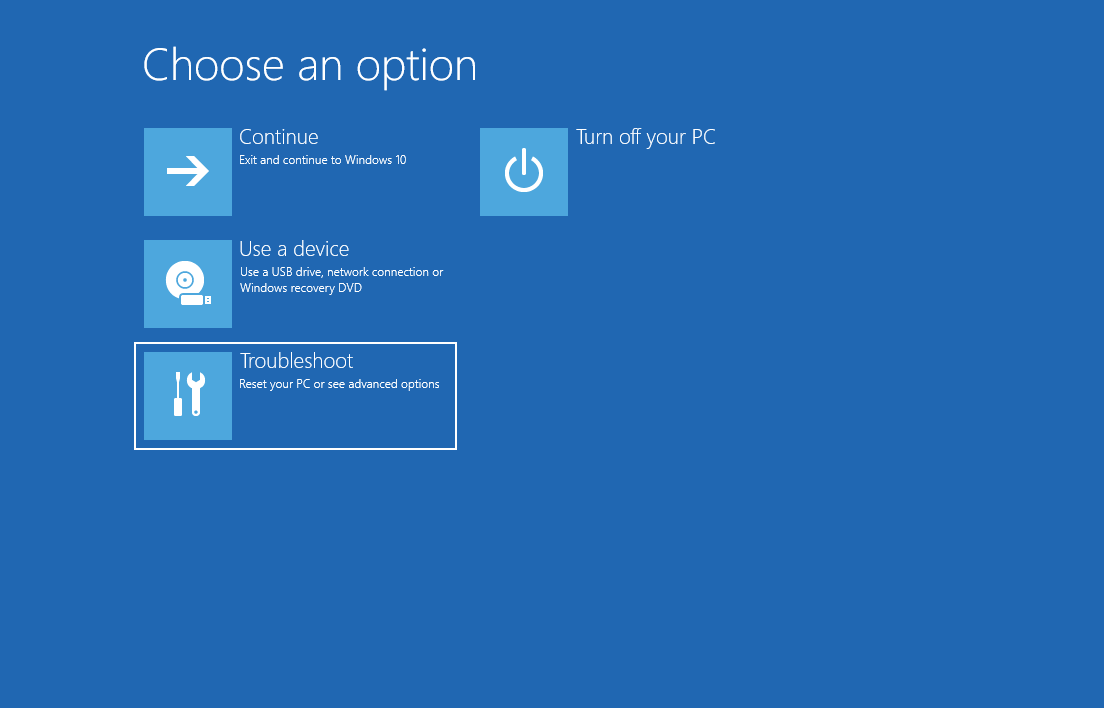
- Select
Troubleshoot
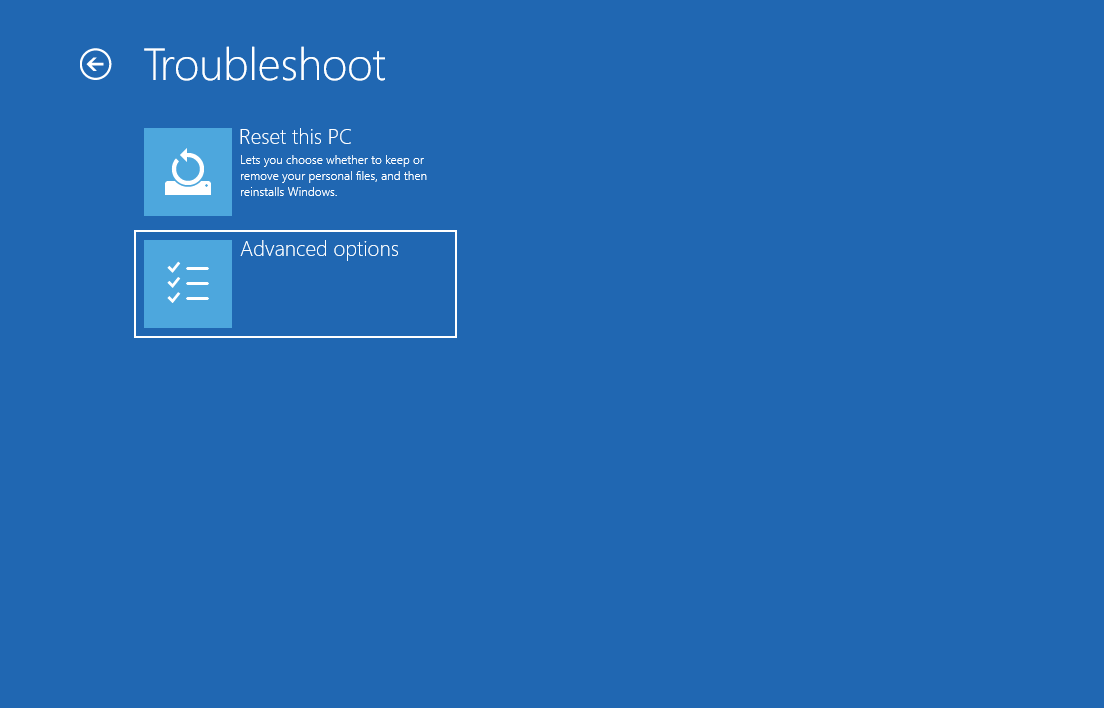
- Then select
Advanced options
- Select
UEFI Firmware Settings
- Hit
Restart
- macOS-based computers
Hardware-assisted virtualization is a hit or miss on Apple computers, as there is no way to access the firmware on these computers. Apple users can jump to the section Make sure that hardware-assisted virtualization is enabled to check whether this feature is activated or not on their particular model.
- Other computers
Make sure the targeted computer is shut down.
During the POST phase, you need to press a certain key to access the firmware configuration tool for your motherboard, which is part of your BIOS or UEFI.
Just after pressing the power-on, press one the following common keystrokes are F2 or Del, depending on your model.
Do not hesitate to repeatedly press the key to make sure it is registered {is.info}
Hardware manufacturers could not agree on a common keystroke to access the firmware configuration tool, so, if the given keys do not work out for you, please have a look at the documentation provided by the manufacturer of your computer. {is.info}
Modify the firmware configuration
to be done
Make sure that hardware-assisted virtualization is enabled
to be done
-
Windows
-
macOS
-
Linux
Failing to activate hardware-assisted virtualization will make running virtual machines extremly slow, if possible at all. If, for some reasons, it cannot be activated on your computer, you would be better off picking a Linux distribution which doesn't require it, such as Debian.
{.is-warning}
If the activation is successful, you can go to the next section to prepare an installation medium.